Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being and quality of life. The gut, or digestive tract, plays a crucial role in processing food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. Moreover, it houses a significant portion of your immune system and influences various aspects of your health, including mental clarity, immune function, and even skin health. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore practical tips for nurturing a healthy gut, including dietary choices, lifestyle adjustments, and other strategies to support optimal digestive function.
Understanding the Gut and Its Importance
Before diving into specific tips, it’s essential to understand why gut health matters. The gut, often referred to as the “second brain” is a complex system of organs, including the stomach, intestines, and associated glands, that work together to digest food and absorb nutrients. The gut microbiome, a community of trillions of microorganisms residing in the intestines, plays a pivotal role in maintaining gut health. These microorganisms help break down food, produce essential nutrients, and protect against harmful pathogens.
A healthy gut is characterized by a balanced microbiome, proper digestion, and efficient nutrient absorption. Imbalances in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can lead to a range of health issues, including digestive disorders, autoimmune diseases, and mental health conditions.

1. Eat a Diverse Range of Natural Foods
A diverse diet is crucial for a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced diet supports gut health and overall well-being. Different foods provide various types of nutrients and fibers that support the growth of a broad range of beneficial bacteria. A healthy diet should include adequate fiber, protein, healthy fats, and vitamins. Aim to include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes in your diet. Avoid processed foods and excessive sugar for optimal health. Each food type offers unique benefits:
Fruits and Vegetables:
Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables also provide dietary fiber that promotes the growth of healthy gut bacteria.
Whole Grains:
Whole grains such as oats, quinoa, and brown rice contain prebiotics, which feed beneficial gut bacteria and enhance their activity.
Nuts and Seeds:
These are excellent sources of healthy fats and fiber, both of which support gut health.
Legumes:
Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are high in fiber and prebiotics that nourish beneficial gut microbes.
Read Food Labels and Identify Hidden Sugars and Additives in Processed Foods
Reading food labels is an important aspect of a healthy diet and helps identify hidden sugars and additives in processed foods. Processed foods may contain hidden sugars and additives. By carefully reading labels, you can avoid high sugar content and harmful additives. Sugar can appear under various names (e.g., fructose, glucose syrup) on labels. Additives and preservatives are also listed. Understanding these details helps in making healthier food choices.
Highly processed foods and excessive sugar intake can negatively impact gut health. Processed foods often contain artificial additives, preservatives, and high levels of sugar, which can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and contribute to inflammation.
To support a healthy gut, focus on whole, unprocessed foods and limit your consumption of sugary snacks, sodas, and pre-packaged meals.
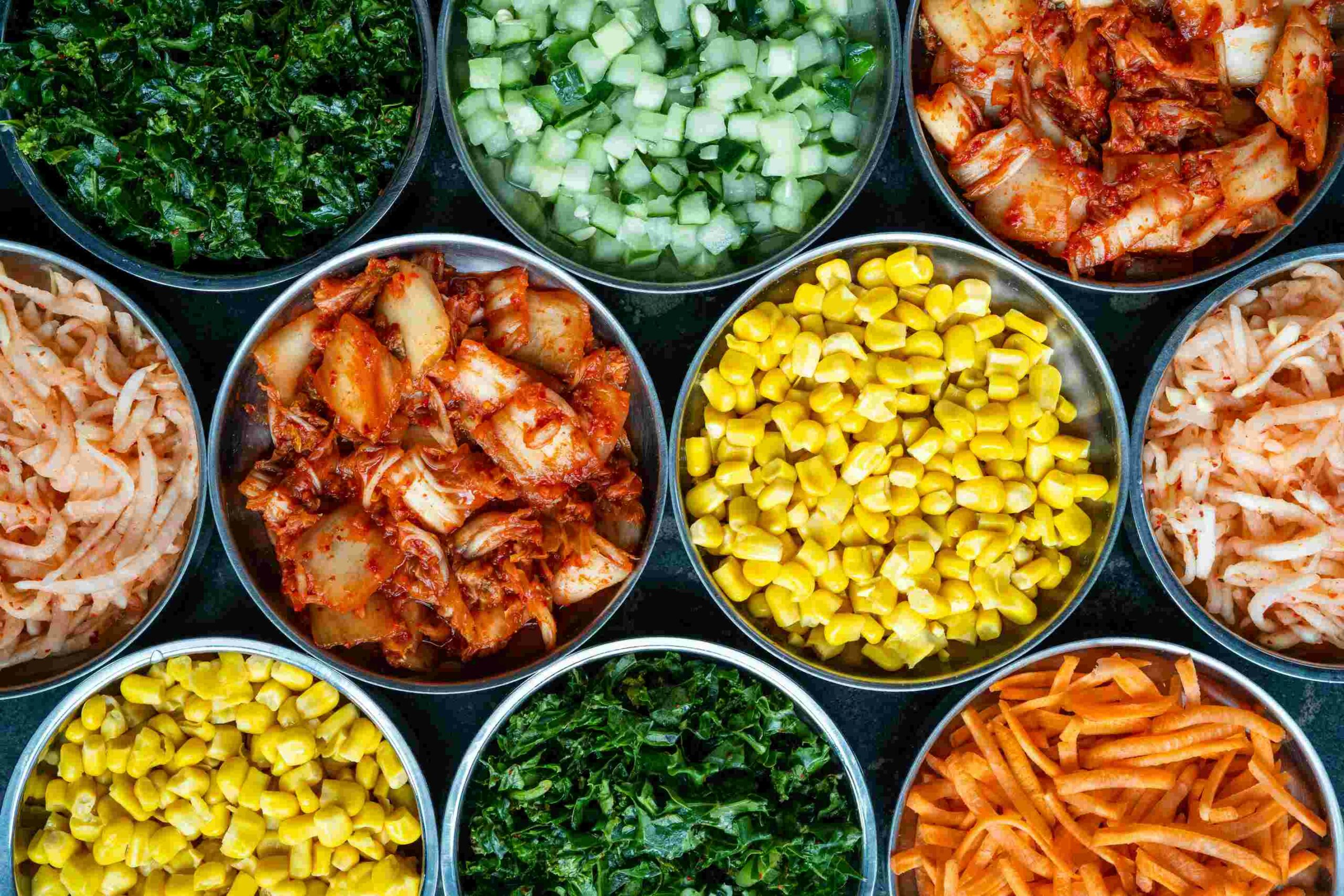
2. Incorporate Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are rich in beneficial bacteria that support gut health. Incorporate a variety of fermented foods into your diet, such as
Kimchi, a Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, usually cabbage and radishes.
Sauerkraut, fermented cabbage that provides probiotics and fiber.
Miso, a Japanese seasoning made from fermented soybeans.
Adding these foods to your diet can help enhance the diversity and balance of your gut microbiome.
3. Incorporate Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics are essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome.
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods. They help restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut flora. Common sources of probiotics include sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, and tempeh. Adding these foods to your diet can help improve digestion and boost your immune system.
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that act as food for beneficial bacteria. They are found in foods such as garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, and leeks. Consuming prebiotic-rich foods can enhance the growth and activity of probiotics in the gut.

4. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is vital for digestive health. Water aids in the digestion of food and helps dissolve nutrients so they can be absorbed more effectively. It also prevents constipation by keeping the stool soft and facilitating its passage through the intestines.
Aim to drink at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water per day. Adjust your intake based on factors such as activity level, climate, and individual needs. Herbal teas and water-rich fruits and vegetables also contribute to your hydration needs.
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can have a profound impact on gut health. Stress triggers the release of hormones and chemicals that can disrupt gut motility, increase inflammation, and alter the gut microbiome.
Incorporate stress-management techniques into your daily routine to support a healthy gut. Consider practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity. These methods can help reduce stress and improve overall gut health. Read more about stress in this article.
6. Get Enough Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy gut. During sleep, the body performs essential repair and regeneration processes, including those related to gut function. Poor sleep patterns can disrupt the gut microbiome and lead to digestive issues.
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establish a regular sleep routine, create a relaxing bedtime environment, and limit exposure to screens before bedtime to promote better sleep.

7. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity supports gut health by promoting healthy digestion and reducing inflammation. Exercise stimulates the movement of the intestines, helping to prevent constipation and improve overall digestive function.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. Activities such as walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming can benefit gut health and contribute to overall well-being.
8. Avoid Overuse of Antibiotics
Antibiotics are designed to kill harmful bacteria, but they can also disrupt the balance of beneficial gut bacteria. Overuse or misuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance and negatively impact gut health.
Use antibiotics only when prescribed by a healthcare professional and follow the prescribed dosage and duration. If you need to take antibiotics, consider incorporating probiotics into your diet to help restore the balance of gut bacteria.
9. Practice Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves paying attention to your food and the eating experience. It can improve digestion by encouraging you to eat slowly, chew your food thoroughly, and savor each bite. Mindful eating can also help prevent overeating and support healthy weight management.
Set aside time for meals, eat without distractions, and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Enjoy a variety of flavors and textures, and focus on the sensory experience of eating.
10. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact gut health. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders and can disrupt the gut microbiome. Excessive alcohol intake can lead to inflammation, gut permeability issues, and imbalances in gut bacteria.
If you smoke, seek support to quit, and limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels. For women, moderate drinking is defined as up to one drink per day, and for men, up to two drinks per day.
11. Address Food Intolerances and Allergies
Food intolerances and allergies can affect gut health and cause digestive discomfort. Common culprits include lactose, gluten, and certain additives. If you suspect a food intolerance or allergy, consult with a healthcare professional to identify and manage the issue.
Consider keeping a food diary to track symptoms and identify potential triggers. Eliminate or reduce problematic foods from your diet and seek alternative sources of nutrients as needed.
12. Avoid Excessive Use of Laxatives
While laxatives can provide temporary relief from constipation, their overuse can disrupt normal bowel function and harm the gut microbiome. Relying on laxatives regularly can lead to dependency and exacerbate digestive issues.
Instead, focus on dietary and lifestyle changes to promote regular bowel movements. Increase fiber intake, stay hydrated, and incorporate physical activity into your routine to support natural digestion.
13. Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you experience persistent digestive issues or suspect a gut health problem, consult with a healthcare professional. A doctor or registered dietitian can provide personalized advice, conduct diagnostic tests, and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.

The Connection Between Gut Health and Psychological Health
Mental Health and Gut Microbiome: The Effects of Gut Health on Mood, Anxiety, and Depression
Recent research has highlighted the significant impact of the gut microbiome on mood and mental health. The gut microbiome, the community of trillions of microorganisms residing in the gut, communicates continuously with the brain through what is known as the gut-brain axis. Understanding how gut health affects mood, anxiety, and depression helps clarify this crucial connection.
Impact on Mood:
Imbalances in the gut microbiome can affect brain chemicals and hormones. For example, serotonin and other neurotransmitters are regulated by gut bacteria. An imbalanced microbiome can lead to lower serotonin levels and depressive symptoms. Additionally, certain gut bacteria may produce chemicals that affect inflammation and stress hormones, potentially impacting mental health.
Effects on Anxiety and Depression:
Studies have shown that imbalances in the gut microbiome may increase the risk of anxiety and depression. The gut-brain axis allows gut bacteria to interact with the brain, influencing stress responses and mood. Inflammation in the gut is also linked to mental health issues. Probiotics and prebiotics can help balance the gut microbiome and improve mood.
Gut-Brain Axis: How Signals Between the Gut and Brain Interact
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain. This system regulates interactions through nerve pathways, hormones, and chemical signals, affecting both gut and brain functions.
Signal Pathway:
Nerve cells in the gut send signals to the brain via the vagus nerve. These signals affect various brain functions such as mood, stress response, and digestive processes. Additionally, gut microbiome influences this communication through chemical signals. For example, some gut bacteria can modulate stress hormone levels.
Research and Findings:
Studies have confirmed the effects of the gut-brain axis on mental health. Specifically, an imbalanced gut microbiome is associated with various mood disorders and mental health issues. This highlights the potential benefits of maintaining gut health for improving mental well-being.

Differences in Gut Health Between Men and Women
Women and Gut Health: The Effects of Hormonal Cycles on Gut Health
Women’s gut health can be influenced by hormonal cycles and menstrual processes. Hormonal changes can affect gut motility and microbiome balance.
Effects of Hormonal Cycles:
Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone can impact gut health. Changes in estrogen levels can alter gut motility and digestive functions. For instance, some women experience constipation or diarrhea during their menstrual cycle.
Gut and Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can affect the gut microbiome and lead to digestive issues. Hormonal changes can also impact inflammation levels in the gut. Managing hormonal changes related to gut health is important for women’s overall well-being.
Men and Gut Health: Factors Affecting Gut Health in Men
Men’s gut health may be influenced by different factors compared to women. Genetic factors, lifestyle, and hormones play significant roles.
Genetic and Lifestyle Factors:
Men’s genetic makeup and lifestyle can impact gut health. For example, higher stress levels in men may lead to imbalances in the gut microbiome. Dietary habits and physical activity levels also play a role in men’s gut health.
Role of Hormones:
Testosterone levels in men can affect gut health. Low testosterone levels may disrupt the gut microbiome and lead to digestive issues. Understanding the relationship between hormonal imbalances and gut health is important for maintaining men’s health.
Common Habits That Harm Gut Health
Inadequate Fiber Intake: The Effects of Fiber Deficiency on Gut Health
Fiber is crucial for gut health. Inadequate fiber intake can lead to digestive problems and gut issues.
Role of Fiber:
Fiber promotes bowel regularity, increases stool volume, and supports digestion. A lack of fiber can lead to constipation, hemorrhoids, and other digestive problems.
Sources of Fiber:
Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are rich in fiber. Including these foods in your diet can support gut health.
Fast Eating Habits: The Negative Effects of Eating Quickly on Digestion
Fast eating habits can negatively impact the digestive system and lead to various health issues.
Digestive Issues:
Eating too quickly can result in insufficient chewing of food, making digestion more difficult and leading to gas, bloating, and other digestive issues.
Eating Slowly:
Eating slowly allows the digestive system to process food properly and helps the brain receive satiety signals. This can prevent overeating and reduce digestive problems.
Insufficient Physical Activity: How Lack of Exercise Affects Gut Health
Physical activity supports gut health. Lack of exercise can contribute to various digestive problems.
Role of Exercise:
Regular exercise promotes bowel movement and supports digestive system function. It can also positively influence the gut microbiome.
Exercise Recommendations:
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week to support gut health. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can improve digestive function.

17. Herbal Solutions for Supporting Gut Health
Ginger and Mint: Herbal Remedies for Digestive Issues
Ginger and mint are effective herbal remedies for digestive problems.
Ginger:
Ginger is traditionally used to alleviate digestive issues. It can soothe the digestive system and reduce nausea. Ginger tea or fresh ginger can benefit the digestive system.
Mint:
Mint can aid digestion and relieve stomach discomfort. It can reduce gas and soothe the digestive system. Mint tea or fresh mint leaves can help manage digestive issues.
Chamomile and Oregano: Other Herbs for Supporting Gut Health
Chamomile and oregano are additional herbal solutions for gut health.
Chamomile:
Chamomile has soothing properties and can reduce inflammation in the digestive system. Chamomile tea can relieve stomach cramps and support digestion.
Oregano:
Oregano has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It can aid digestion and support gut health. Oregano tea or dishes seasoned with oregano can benefit the digestive system.
Conclusion
A healthy gut is crucial for overall health and quality of life. To support gut health, there are several key tips related to diet, lifestyle, and habits that should be considered.
Nutrition:
Consuming fiber-rich foods helps ensure proper digestive function. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes support adequate fiber intake. Additionally, probiotic and prebiotic foods can help balance the gut microbiome.
Lifestyle:
Adequate water intake, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep positively impact gut health. Exercise promotes bowel movement, while adequate sleep supports digestive processes.
Habits:
Eating slowly and managing stress can reduce digestive issues. Also, avoiding hidden sugars and additives in processed foods helps maintain gut health.
By following these tips, you can support your gut health and enhance your overall quality of life
Subscribe to our newsletter, follow us on social media to let us know how you’re working towards a balanced life!
Progesterone
What is Progesterone? Progesterone is a steroid...
Understanding Estrogen
Estrogen is one of the most crucial hormones for...
Hashimoto’s Disease
Introduction Hashimoto's disease, or...
Understanding the Thyroid: Functions, Diseases, and Dietary Considerations
Introduction The thyroid gland plays a...
TMAO: What It Is, Its Effects on Health, and Management Strategies
Introduction Trimethylamine N-oxide...
Understanding the Nervous System: Functions, Diseases, and Health Tips
The nervous system is a highly intricate and...
Understanding Oxidative Stress: Its Causes, Health Impacts, and Management
Oxidative stress is a biological condition that...
Reconsidering Extreme Diets: Why Paleo, Raw, and Vegan Might Not Be the Best Choice
In today’s fast-paced world, many people are...
How to Eat in the Right Order for Optimal Health
The order in which we eat our food can have a...