What is Lipedema?
Lipedema is a chronic medical condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat, primarily in the legs, hips, buttocks, and, sometimes, the arms. Unlike regular obesity, the fat distribution in lipedema is often disproportionate, and it is resistant to diet and exercise. This condition is typically painful, causing tenderness in the affected areas, and may be accompanied by easy bruising. Though the cause of lipedema is not entirely understood, it is believed to have a genetic and hormonal basis.
Who is Affected by Lipedema?
Lipedema predominantly affects women, with an estimated 11% of the female population experiencing this condition to varying degrees. Men are rarely affected. Lipedema commonly manifests during periods of significant hormonal change, such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, further suggesting a hormonal link.
Why is Lipedema More Common in Women?
The higher prevalence of lipedema in women is believed to be linked to hormonal fluctuations, particularly those involving estrogen. Estrogen, the primary female hormone, influences fat distribution in the body, particularly in areas like the hips, thighs, and buttocks, which are the regions most affected by lipedema. During life stages like puberty and pregnancy, where estrogen levels fluctuate significantly, women are more vulnerable to developing lipedema. Genetics may also play a role, as lipedema often runs in families.
Prevention Strategies for Lipedema
Although the exact cause of lipedema is unclear, taking proactive steps in maintaining a healthy lifestyle can be beneficial in preventing its onset or slowing its progression. Strategies include:
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
While lipedema is not directly caused by obesity, being overweight can worsen symptoms and increase discomfort.
Regular Physical Activity
Incorporating low-impact exercises helps maintain circulation and muscle tone, which may slow the progression of fat accumulation.
Lymphatic Health
Ensuring that the lymphatic system functions optimally through manual lymph drainage (MLD) or massage may help prevent excessive fluid retention, often associated with lipedema.

Non-Medication-Based Treatments for Lipedema
Lipedema cannot be cured with medication, but there are several non-surgical and natural management options that can alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
Compression Therapy
Wearing compression garments, such as compression stockings, helps support the lymphatic system, reduce swelling, and improve blood flow.
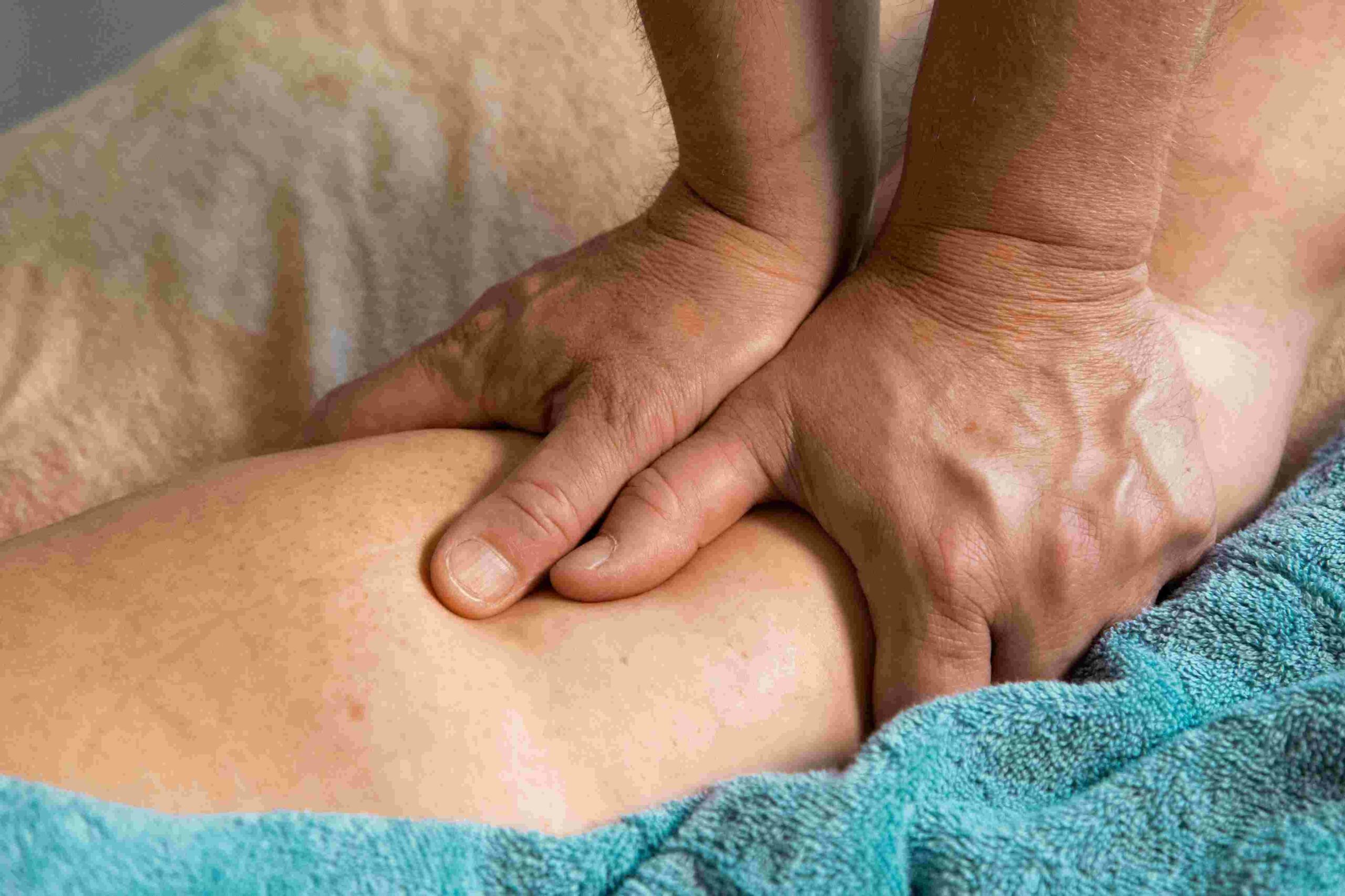
Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD)
This specialized massage technique focuses on moving fluid out of the affected areas, reducing pain and swelling.
Recommended Physical Activities for Lipedema
Exercise is vital for managing lipedema. However, due to the sensitivity and discomfort in the affected areas, not all forms of physical activity are suitable. The following low-impact exercises are recommended:
Swimming and Aquatic Exercises
Water-based activities are gentle on the joints and provide resistance, making them ideal for individuals with lipedema. Swimming helps improve circulation without putting excessive strain on the body.
Walking
Brisk walking can improve circulation and promote lymphatic drainage, reducing swelling in the legs.
Cycling
Cycling is another low-impact exercise that strengthens the lower body muscles and boosts circulation.
Yoga
Gentle yoga movements can enhance flexibility and support lymphatic flow, relieving tension in the affected areas.

Dietary Considerations for Lipedema
Although lipedema is not caused by diet, certain dietary changes can help manage the symptoms. A well-balanced diet that focuses on reducing inflammation, supporting lymphatic health, and maintaining a healthy weight is essential. Consider the following:
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and fatty fish (e.g., salmon), can help reduce inflammation. Also, fruits and vegetables like berries, spinach, and avocados, which contain antioxidants, are beneficial for reducing oxidative stress and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
High-Fiber Foods
Consuming fiber-rich foods like quinoa, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens helps promote digestive health and support weight management, which may ease lipedema symptoms.
Avoid Processed Foods and Refined Sugars
Processed foods and sugary snacks increase inflammation and contribute to fluid retention, worsening lipedema symptoms.
Beneficial Herbal Teas for Lipedema
Certain herbal teas may support lymphatic function, reduce swelling, and promote detoxification. Consider adding the following teas to your routine:
Green Tea
Rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties, green tea can support weight management and improve circulation.
Dandelion Root Tea
This tea acts as a natural diuretic, helping reduce fluid retention and bloating, which can exacerbate lipedema symptoms.
Ginger Tea
Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger tea can help improve circulation and reduce swelling in the affected areas.
Foods to Avoid with Lipedema
Certain foods can worsen lipedema symptoms by promoting inflammation and fluid retention. Avoid the following:
Gluten-Containing Foods
Gluten may contribute to inflammation in sensitive individuals, worsening lipedema symptoms.
Dairy Products
Dairy can cause inflammation and fluid retention, especially in individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy sensitivity.
High-Sodium Foods
Excess salt causes fluid retention, leading to increased swelling in the affected areas.

Additional Therapies: Massage, Dry Brushing, and Other Techniques
In addition to exercise and diet, certain physical therapies can help manage lipedema symptoms:
Dry Brushing
This technique involves using a soft-bristled brush to stimulate the lymphatic system and promote circulation. Dry brushing, performed in upward motions toward the heart, helps move lymph fluid and reduce swelling in the affected areas.
Massage Therapy
Regular massages, particularly lymphatic drainage massages, can alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and improve overall circulation in individuals with lipedema.
Cold Showers and Water Therapy
Alternating between warm and cold water during showers helps stimulate the lymphatic system and improve blood flow, potentially reducing fluid retention and discomfort.
Conclusion
Lipedema is a challenging condition that primarily affects women, often manifesting during hormonal shifts. While it cannot be cured with medication, adopting a holistic approach that includes proper diet, regular exercise, physical therapies, and self-care strategies can significantly improve symptoms and prevent further progression. By focusing on maintaining lymphatic health, reducing inflammation, and supporting circulation, individuals with lipedema can lead healthier, more comfortable lives.
Subscribe to our newsletter, follow us on social media to let us know how you’re working towards a balanced life!
Oral Health: Causes, Prevention, and the Role of Nutrition
Oral health is often a neglected part of our...
Food Allergies: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Food allergies and sensitivities are...
Unintentional Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss can be distressing,...
The Negative Impacts of Plastic Usage on Health and the Environment
Plastic has revolutionized modern life,...
The Impact of Social Media on Body Image: How It Affects Women’s Health
Social media has transformed how we connect,...
Why Women Need Nutrition Counseling Beyond Weight Loss
Women face unique challenges when it comes to...
The Benefits of Journaling for Mental Health
Journaling has gained recognition as a powerful...
Minimalism and Health: The Effects of a Minimalist Lifestyle on Mental and Physical Well-being
Living in a world where consumerism and constant...
Physical activity: Cardio, Strength Training, Yoga, and Pilates
Engagement in regular physical activity is...










